The presidency of the United States is a position of immense power and responsibility, shaping the course of the nation's history. Over ...
The presidency of the United States is a position of immense power and responsibility, shaping the course of the nation's history. Over the years, the occupants of the Oval Office have played pivotal roles in advancing American society, economy, and international relations. In this blog post, we will journey through time and highlight one significant political accomplishment of each U.S. President, from the first president to the current one.
George Washington (1789-1797) - Establishment of the Presidency:
George Washington set the precedent for the role and responsibilities of the presidency, solidifying the foundations of the young nation and ensuring the peaceful transfer of power through his two terms.
John Adams (1797-1801) - Avoidance of War with France:
President Adams successfully maintained peace with France by negotiating the Treaty of Mortefontaine, resolving a potential conflict known as the "Quasi-War" and preserving American neutrality during European conflicts.
Thomas Jefferson (1801-1809) - Louisiana Purchase:
Jefferson's administration doubled the size of the United States through the acquisition of the vast Louisiana Territory from France in 1803, expanding American influence and opening up new opportunities for westward expansion.
James Madison (1809-1817) - Leadership during the War of 1812:
President Madison's leadership during the War of 1812 demonstrated American resilience, defending national sovereignty and asserting the young nation's independence from Great Britain.
James Monroe (1817-1825) - Monroe Doctrine:
Monroe's articulation of the Monroe Doctrine in 1823 established the United States as the dominant power in the Western Hemisphere, declaring opposition to European colonization and intervention in the Americas.
John Quincy Adams (1825-1829) - Advocacy for Infrastructure:
Adams prioritized internal improvements, proposing ambitious infrastructure projects such as roads, canals, and a national university, laying the groundwork for future development.
Andrew Jackson (1829-1837) - Expansion of Voting Rights:
Jackson championed the expansion of voting rights to non-landowning white males, significantly increasing political participation and establishing a more inclusive democracy.
Martin Van Buren (1837-1841) - Creation of an Independent Treasury System:
Van Buren established an independent treasury system, separating government funds from private banks, thereby ensuring greater financial stability and reducing the risk of economic crises.
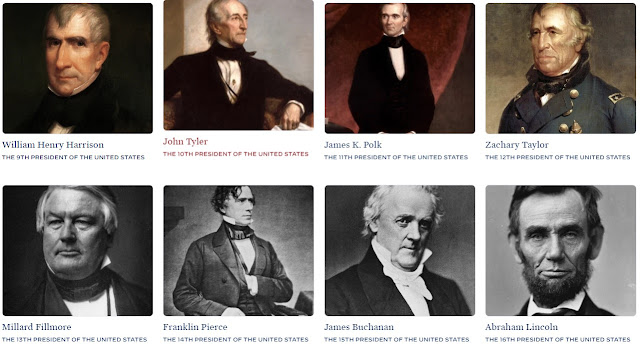
William Henry Harrison (1841) - Opening New Territories:
Although Harrison's presidency was cut short by his untimely death, he played a significant role in expanding U.S. territories by promoting westward settlement and opening the Oregon Trail.
John Tyler (1841-1845) - Annexation of Texas:
Tyler played a crucial role in the annexation of Texas, paving the way for its eventual statehood and expanding American influence in the Southwest.
James K. Polk (1845-1849) - Mexican-American War and Western Expansion:
Polk's administration oversaw the Mexican-American War, leading to the acquisition of vast territories, including California, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, and parts of New Mexico and Colorado.
Zachary Taylor (1849-1850) - California Statehood:
Taylor supported California's admission to the Union as a free state, helping to maintain a delicate balance between free and slave states.
Millard Fillmore (1850-1853) - Compromise of 1850:
Fillmore played a key role in passing the Compromise of 1850, which aimed to ease tensions between free and slave states, delaying the eruption of the Civil War.
Franklin Pierce (1853-1857) - Gadsden Purchase:
Pierce's administration negotiated the Gadsden Purchase, acquiring a strip of land in present-day Arizona and New Mexico, facilitating the construction of a southern transcontinental railroad.
James Buchanan (1857-1861) - Dred Scott Decision:
Buchanan faced the challenge of the growing tensions over slavery, and although his presidency is marred by inaction, his appointment of Supreme Court justices led to the infamous Dred Scott decision, which declared that enslaved individuals were property and not citizens.
Abraham Lincoln (1861-1865) - Emancipation Proclamation and Civil War Leadership:
Lincoln's presidency was defined by his leadership during the Civil War and his signing of the Emancipation Proclamation in 1862, which declared enslaved individuals in Confederate territories to be free, setting the stage for the eventual abolition of slavery.
Andrew Johnson (1865-1869) - Reconstruction Efforts:
Johnson oversaw the tumultuous period of Reconstruction after the Civil War, working towards reuniting the nation and extending civil rights to formerly enslaved individuals through the passage of the Civil Rights Act of 1866.
Ulysses S. Grant (1869-1877) - Civil Rights Enforcement and Reconstruction Policies:
Grant's presidency marked a commitment to civil rights, as he advocated for and signed the Enforcement Acts to protect African American voting rights and implemented Reconstruction policies in the South.
Rutherford B. Hayes (1877-1881) - Compromise of 1877 and Civil Service Reform:
Hayes oversaw the Compromise of 1877, which resolved the disputed presidential election and marked the end of Reconstruction. He also initiated civil service reforms to combat corruption and patronage.
James A. Garfield (1881) - Advocacy for Civil Service Reform:
Garfield, though serving a tragically short presidency due to his assassination, was a strong proponent of civil service reform, advocating for merit-based appointments and an end to political patronage.
Chester A. Arthur (1881-1885) - Pendleton Civil Service Reform Act:
Arthur successfully championed the Pendleton Civil Service Reform Act of 1883, establishing a merit-based system for government employment and reducing political interference in appointments.
Grover Cleveland (1885-1889, 1893-1897) - Interstate Commerce Act and Tariff Reform:
Cleveland signed the Interstate Commerce Act of 1887, establishing regulatory oversight of the railroad industry, and advocated for lower tariffs, promoting fair trade practices and consumer benefits.
Benjamin Harrison (1889-1893) - Sherman Antitrust Act:
Harrison signed the Sherman Antitrust Act in 1890, aimed at curbing monopolistic practices and promoting fair competition in business, setting the foundation for future antitrust legislation.
William McKinley (1897-1901) - Spanish-American War and Expansion:
McKinley led the United States into the Spanish-American War in 1898, resulting in the acquisition of territories such as Puerto Rico, Guam, and the Philippines, expanding American influence beyond its continental borders.
Theodore Roosevelt (1901-1909) - Progressive Reforms and Conservation:
Roosevelt's presidency was marked by significant progressive reforms, including the Pure Food and Drug Act, the establishment of the National Park System, and his advocacy for trust-busting to regulate monopolies and promote fair competition.
William Howard Taft (1909-1913) - Dollar Diplomacy:
Taft implemented a foreign policy strategy known as "Dollar Diplomacy," which aimed to promote U.S. economic interests abroad by encouraging American investment in Latin America and East Asia.
Woodrow Wilson (1913-1921) - League of Nations and Women's Suffrage:
Wilson played a pivotal role in establishing the League of Nations, a precursor to the United Nations, with the aim of promoting international cooperation and preventing future conflicts. He also supported and signed the 19th Amendment, granting women the right to vote.
Warren G. Harding (1921-1923) - Return to Normalcy:
Harding sought to restore stability and normalcy after the tumultuous post-World War I period, focusing on economic recovery, reducing government intervention, and advocating for disarmament.
Calvin Coolidge (1923-1929) - Economic Prosperity and Tax Cuts:
Coolidge presided over a period of economic prosperity known as the "Roaring Twenties." He championed pro-business policies, including tax cuts, which fueled economic growth and innovation.
Herbert Hoover (1929-1933) - Response to the Great Depression:
Hoover grappled with the onset of the Great Depression and implemented various relief measures, such as the creation of the Reconstruction Finance Corporation, to stabilize the economy and provide assistance to struggling Americans.
Franklin D. Roosevelt (1933-1945) - New Deal and World War II Leadership:
FDR's presidency was marked by his implementation of the New Deal, a series of programs and reforms aimed at addressing the Great Depression. He also guided the nation through World War II, mobilizing the country's resources and leading the Allies to victory.
Harry S. Truman (1945-1953) - Truman Doctrine and Marshall Plan:
Truman's presidency saw the implementation of the Truman Doctrine, which provided aid to countries threatened by communism, and the Marshall Plan, which provided economic assistance to help rebuild war-torn Europe.
Dwight D. Eisenhower (1953-1961) - Interstate Highway System and Space Exploration:
Eisenhower championed the construction of the Interstate Highway System, promoting economic growth and facilitating transportation across the nation. He also launched the space race by establishing NASA in response to the Soviet Union's Sputnik.
John F. Kennedy (1961-1963) - Civil Rights Advocacy and the Space Program:
Kennedy's presidency witnessed significant advancements in the civil rights movement, with his support for desegregation efforts and his proposal for comprehensive civil rights legislation. He also set the ambitious goal of landing a man on the moon, leading to the Apollo program.
Lyndon B. Johnson (1963-1969) - Civil Rights Act and Great Society Programs:
Johnson signed the landmark Civil Rights Act of 1964, outlawing racial segregation, and implemented his Great Society programs, which aimed to address poverty, healthcare, and education disparities in the United States.
Richard Nixon (1969-1974) - Opening Relations with China and Environmental Protections.
Gerald Ford (1974-1977) - Nixon Pardon and Economic Stabilization:
Ford granted a full pardon to Richard Nixon, promoting national healing and moving the country past the Watergate scandal. He also implemented economic policies to address inflation and stabilize the economy.
Jimmy Carter (1977-1981) - Camp David Accords and Human Rights Advocacy:
Carter brokered the historic Camp David Accords in 1978, facilitating peace between Israel and Egypt. He also prioritized human rights on the international stage, promoting democracy and advocating for the rights of oppressed individuals.
Ronald Reagan (1981-1989) - Reaganomics and Cold War Diplomacy:
Reagan implemented economic policies known as "Reaganomics," which aimed to stimulate economic growth through tax cuts and deregulation. He also pursued a strong anti-communist agenda, leading to increased tensions with the Soviet Union and eventually contributing to the end of the Cold War.
George H. W. Bush (1989-1993) - Gulf War Coalition and Americans with Disabilities Act:
Bush built an international coalition to repel Iraq's invasion of Kuwait in 1991, demonstrating strong diplomatic leadership. He also signed the Americans with Disabilities Act into law, prohibiting discrimination against individuals with disabilities.
Bill Clinton (1993-2001) - Welfare Reform and Balanced Budget:
Clinton signed the Personal Responsibility and Work Opportunity Reconciliation Act of 1996, which introduced welfare reform measures aimed at promoting self-sufficiency. Under his administration, the United States also achieved a balanced federal budget for the first time in decades.
George W. Bush (2001-2009) - War on Terror and No Child Left Behind Act:
Bush led the United States through the aftermath of the September 11 attacks and initiated the global "War on Terror." He also championed the No Child Left Behind Act, aiming to improve education standards and accountability.
Barack Obama (2009-2017) - Affordable Care Act and Economic Recovery:
Obama signed the Affordable Care Act, expanding access to healthcare and implementing significant healthcare reforms. He also guided the nation through the economic recovery following the 2008 financial crisis, overseeing the implementation of stimulus measures.
Donald Trump (2017-2021) - Tax Reform and Deregulation:
Trump signed the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017, which aimed to stimulate economic growth through tax reductions for individuals and corporations. His administration also focused on deregulation to promote business expansion and streamline government processes.
Joe Biden (2021-present) - COVID-19 Response and Infrastructure Plan:
Biden has prioritized the response to the COVID-19 pandemic, implementing vaccine distribution efforts and economic relief measures. He has also proposed an ambitious infrastructure plan to modernize American infrastructure and create jobs.
From the establishment of the presidency by George Washington to the current administration of Joe Biden, each U.S. President has left their mark through important political accomplishments. These achievements have shaped the nation's development, influenced international relations, and advanced societal progress. By recognizing and understanding these accomplishments, we gain a deeper appreciation for the impact of leadership on the trajectory of the United States.






No comments